Resource Pages
Jun 30, 2014
Ninety-Nine Percent of the Ocean's Plastic Is Missing ... May already be in food chain
Please continue reading from: Ninety-Nine Percent of the Ocean's Plastic Is Missing
// b Slashdot
The Deadliest Ebola Outbreak in History is Happening Right Now — And It's Getting Worse [
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), the epidemic has so far killed more than 390 people and afflicted more than 600 in Liberia, Sierra Leone and Guinea, where the current outbreak originated. That's deadlier than the virus's first outbreak in 1976 near the Ebola River in the current-day Democratic Republic of Congo which killed 280 people.
Resources are also wearing thin. "The epidemic is out of control," Bart Janssens, the director of operations for Médecins Sans Frontières (the French version of Doctors Without Borders) said in a statement. "We have reached our limits. Read More
New water-based organic battery is cheap, rechargeable and eco-friendly
Lithium-ion batteries have made portable, rechargeable electronics commonplace. Unfortunately, they do have some glaring drawbacks, including heat issues, being made with rare, toxic elements, and the fact the technology doesn't scale up very well, which limits applications. A team of scientists at the University of Southern California (USC) is working on an alternative in the form of a water-based organic battery that is not only cheaper and more environmentally friendly, but also holds the potential for scaling up for use in wind and solar power plants as a means to store large amounts of energy. .. Continue Reading New water-based organic battery is cheap, rechargeable and eco-friendly
Jun 29, 2014
For a "higher level of security" German Gov't Cancels Verizon Contract in Wake of U.S. Spying
Fox Business: The German government has canceled a contract with U.S. telecoms firm Verizon Communications Inc as part of an overhaul of its internal communications, prompted by revelations last year of U.S. government spying.
Reports based on disclosures by former U.S. intelligence contractor Edward Snowden alleged Washington had conducted mass surveillance in Germany and had even eavesdropped on Chancellor Angela Merkel's mobile phone.
Berlin subsequently demanded talks with Washington on a "no-spy" deal, but these collapsed after the United States appeared unwilling to give the assurances Germany wanted.
Germany also launched an overhaul of its internal communications and secure government networks. This is one of the first actions involving a U.S. firm to result.
"The pressures on networks as well as the risks from highly developed viruses or Trojans are rising," Germany's Interior Ministry said in a statement on Thursday.
"Furthermore, the ties revealed between foreign intelligence agencies and firms in the wake of the U.S. National Security Agency (NSA) affair show that the German government needs a very high level of security for its critical networks."
http://www.foxbusiness.com/industries/2014/06/26/german-govt-cancels-verizon-contract-in-wake-us-spying-row/
Jun 28, 2014
Major U.S. Retailers to Limit Pesticides That May Be Harmful to Bees
Please read full and follow at: Major U.S. Retailers to Limit Pesticides That May Be Harmful to Bees / Yale Environment 360
Living Global #Water Scarcity: the Four Liter Challenge via @Sustainablog

Sustainablog How much water do you think you use every day? Not just drink… but use for cooking, bathing, and cleaning? 10 gallons? 50? How about 145 gallons (or 550 liters) every day? That's the American average per person… unfortunately, as I learned at this week's Further with Ford conference, that's yet another area in which we in the US indulge ourselves well beyond the rest of the world. Global water scarcity limits some of the world's poorest people to a mere 4 liters – or just a smidge over 1 gallon – a day.
That's right: 4 litres for all of the things mentioned above. No long hot showers, no leaving the water on while brushing your teeth, no taking a few sips and then dumping the rest: that water is very precious for about 800 million people worldwide. Could you do this: live on just four liters a day? Not just a small fraction of what we normally consume, but even a mere 10-12% of the water needed to live at minimal standards of health and wellness?
George McGraw, the founder of DIGDEEP, a non-profit focused on the global water crisis, offered those of us at the "Sustainability Blues" session an opportunity to commit to such a water-scarce lifestyle… for just a few days. See, DIGDEEP hosts the 4 Liter Challenge, an event in October in which those of us who live with vast water wealth commit to "trying on" water poverty for just a few days. The concept: experiencing water scarcity at this level will make it real for us. Please read full and follow at: Living Global Water Scarcity: the Four Liter Challenge
follow @SustainablogTribes ask EPA to intervene in Gogebic iron mine proposal
The tribes told the EPA they believe the open pit mine, which would be located in Ashland and Iron counties, would harm local water resources.
Six Chippewa Indian bands in Wisconsin have asked the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency to evaluate the environmental effects of a proposed iron ore mine in northern Wisconsin before the plan is reviewed by state regulators and another federal agency.
The request is similar to one made before a decision by the EPA in February to review a proposed mining project in Alaska that opponents, including Indian tribes, say would harm nearby fishing stocks.
The tribes told the EPA they believe the open pit mine, which would be located in Ashland and Iron counties, would harm local water resources and pollute waters downstream extending to Lake Superior.
In their petition, the Chippewa tribes asked the EPA to intercede and evaluate the effects of the mine before the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers reviews a mining application.
That review could include an EPA veto of a decision by the Corps or the state over the effects of dredging and digging in or near waterways.
In their May 27 letter, the tribes argued that new state iron mining regulations have been weakened in many ways, for example, by allowing iron mine developers to fill in wetlands and by altering standards for protecting groundwater. The legislative changes had been pushed by the mining company, Gogebic Taconite, as a condition to come to Wisconsin to develop the mine.
The company is proposing to build two open-pit mines up to 1,000 feet deep that would span about four miles.
The tribes include the Bad River band of Lake Superior Chippewa, whose reservation is nearest the project. Tribal Chairman Mike Wiggins Jr. said in a letter to the EPA that sulfide waste rock could make waters acidic, harm fish populations and devastate the largest beds of wild rice on the Great Lakes.
Gogebic has not filed a formal application for a mining permit, and is not expected to in 2014. Once it applies for a permit, the state Department of Natural Resources and Army Corps of Engineers must conduct an environmental review of the project.
The EPA rarely steps in to review under the Clean Water Act. It has decided to evaluate potential projects 29 times over the past 40 years of the law. In 13 of those cases, the agency decided to limit or stop activity that posed an environmental threat.
Please read full and follow at: Tribes ask EPA to intervene in Gogebic iron mine proposal
Germany's Glut of #Renewable #Energy Causing Prices To Plummet
Read more of this story at Slashdot.
Jun 27, 2014
This Weird, Massive Tower May Be the Future of Energy in the U.S.
:strip_icc(1)/https%3A%2F%2Fs3.amazonaws.com%2Fpolicymic-images%2F093ecbfc0104b5b968a199afd65f4f3f82b8ec833069274024cdfad00bbefa76.jpg)
The news: The country's largest freestanding structure will soon start construction — and it's going to be a solar-wind tower. Projected to reach 2,250 feet, it will be considerably taller than other American landmarks like the 1,454-foot Empire State Building. Designed by Maryland-based Solar Wind Energy Tower Inc., the solar-wind hybrid facility just secured funding to build its first model, which is projected to stand near San Luis, Ariz., by 2018.
How it works: A network of sprayers emits a fine mist of water droplets over the upper lip of the structure; the mist subsequently evaporates, absorbing the ambient heat of the surrounding atmosphere (that's the solar component). The result is dense, cool air that rapidly flows to the bottom of the structure. The air reaches up to 50 mph by the time it hits the bottom, where it is diverted outwards through a series of tunnels radiating from the inside of the tube. Read More
EPA calls for stronger toxics laws on heels of TCE report
Please continue reading from: EPA calls for stronger toxics laws on heels of TCE report
// Hazardous Material Magazine
Study: 51% of garden stores sell plants bee killing pesticides
New Chemical Process Could Make Ammonia a Practical Car Fuel [feedly]
// b Slashdot
Air Pollution Can Disrupt Pollinating Insects By Concealing the Scent of Flowers
Jun 26, 2014
Scientists Warn That a Widely Used Pesticide Could Be Worse for Bees Than DDT
TakePart... more than 40 years after the United States Environmental Protection Agency banned DDT, thanks in large part to the publication of Rachel Carson's Silent Spring, a class of agricultural pesticides called neonicotinoids (neonics) poses an even more serious threat to bees, other wildlife, and entire ecosystems, according to a preview of a report to be published next week by an international group of scientists.
"In the case of acute effects alone, some neonics are at least 5,000 to 10,000 times more toxic to bees than DDT," wrote the scientists affiliated with the Task Force on Systemic Pesticides. "The evidence is also clear that neonics pose a serious risk of harm to honey bees and other pollinators."
Studies have implicated neonics in the mass die-off of bees that pollinate a third of the global food supply. Many scientists believe the pesticide is one of several interrelated factors—including disease, parasites, and poor nutrition—responsible for the apian catastrophe that has unfolded over the past decade.
Please continue reading from source at:http://www.takepart.com/article/2014/06/24/are-neonicotinoids-new-ddt-bees-and-other-wildlife
Jun 25, 2014
Neurotoxic pesticides blamed for the world's bee collapse are also harming butterflies, worms, fish and birds
Paris (AFP) - Neurotoxic pesticides blamed for the world's bee collapse are also harming butterflies, worms, fish and birds, said a scientific review that called Tuesday for tighter regulation to curb their use.
Analysing two decades of reports on the topic, an international panel of 29 scientists found there was "clear evidence of harm" from use of two pesticide types, neonicotinoids and fipronil.
And the evidence was "sufficient to trigger regulatory action".
"We are witnessing a threat to the productivity of our natural and farmed environment," said Jean-Marc Bonmatin of France's National Centre for Scientific Research, co-author of the report entitled the Worldwide Integrated Assessment.
Far from protecting food production, these nerve-targeting insecticides known as neonics were "imperilling the pollinators, habitat engineers and natural pest controllers at the heart of a functioning ecosystem."
The four-year assessment was carried out by The Task Force on Systemic Pesticides, which advises the International Union for Conservation of Nature, the world's watchdog on species loss.
Neonics are widely used insecticides whose effects can be instant and lethal, or chronic. Exposure can impair smell and memory in some species, curb procreation, reduce foraging, cause flight difficulties and increase disease susceptibility.
Used for insect pest management in farming, but also in pet flea control, they have been fingered in the recent decline in bees -- crucial pollinators of human food crops -- in Europe, the Americas and Asia.
The latest study says these pesticides, absorbed by plants, are also harming other insect pollinators, fish and birds as they leach into soil and water.
The most affected species were terrestrial invertebrates such as earthworms, which are crucial soil-enrichers, said a press statement.
Bees and butterflies were next, followed by aquatic invertebrates like freshwater snails and water fleas, then birds, and finally fish, amphibians and certain microbes.
"The combination of their widescale use and inherent properties, has resulted in widespread contamination of agricultural soils, freshwater resources, wetlands, non-target vegetation, estuarine and coastal marine systems," the authors wrote.
"This means that many organisms inhabiting these habitats are being repeatedly and chronically exposed to effective concentrations of these insecticides."
Please continue reading from source at:http://news.yahoo.com/pesticides-threaten-birds-bees-alike-study-225404567.html
"There are an estimated 30 million slaves in the world today, more than at any other time in history."
THE AMERICAN INTEREST: Pakistan Has More Than Two Million Slaves
There are an estimated 30 million slaves in the world today, more than at any other time in history. In case you missed it, earlier this month Real Clear World ran a profile of what slave labor looks like in Pakistan today. There are 1.8 million "debt laborers" in the country, and 2.2 million slaves over all (only India and China have more). The debt laborers are kept under the thumb of landlords who sell them back and forth and cook up ways of keeping them in bondage:
"Usually we remain in debt because we take amounts from them [the landlords] for feeding our children and other day to day expenses," he says, sitting outside his home, a mud hut sandwiched between an irrigation channel and the road. Nanji's only contact with the landlord is through the farm manager.
Money rarely changes hands between landlord and tenants. Instead all transactions are recorded in a register maintained by the landlord. Each harvest is meant to pay off part of the debt, but costs—many of which the landlord is meant to bear himself under the few laws that are meant to offer protection to laborers in Pakistan—are added to the debt with interest.
"The actual thing that is keeping people in bondage is the manipulation of the records. The "hari" is illiterate and uneducated and doesn't know how to keep the records," explained Ghulam Hyder, director of the Green Rural Development organization, a Sindh-based group working with bonded laborers, using the Sindhi term for tenant
Pakistan Has More Than Two Million Slaves - The American Interest
http://www.the-american-interest.com/blog/2014/06/22/pakistan-has-more-than-two-million-slaves/
Jun 24, 2014
ROSI solar-powered, mobile water filtration system tested in Tanzania
// Gizmag Emerging Technology Magazine

GO Kin backpacks generate electricity from walking and hiking
// Gizmag Emerging Technology Magazine

World's First Large-Scale Waste-to-Biofuels Facility Opens In Canada
// b Slashdot
Water war bubbling up between California and Arizona - Los Angeles Times
Los Angeles Times...The next water war between California and Arizona won't be such an amusing little affair. And it's coming soon.
The issue still is the Colorado River. Overconsumption and climate change have placed the river in long-term decline. It's never provided the bounty that was expected in 1922, when the initial allocations among the seven states of the Colorado River basin were penciled out as part of the landmark Colorado River Compact, which enabled Hoover Dam to be built, and the shortfall is growing.
The signs of decline are impossible to miss. One is the wide white bathtub ring around Lake Mead, the reservoir behind Hoover Dam, showing the difference between its maximum level and today's. Lake Mead is currently at 40% of capacity, according to the latest figures from the U.S. Bureau of Reclamation, which operates the dam. At 1084.63 feet on Wednesday, it's a couple of feet above its lowest water level since it began filling in 1935.
But the rules governing appropriations from the river are unforgiving and don't provide for much shared sacrifice among the states, or among farmers and city dwellers.
The developing crisis can't be caricatured as farmers versus fish, as it is by Central Valley growers irked at environmental diversions of water into the region's streams. It can't be addressed by building more dams, because reservoirs can't be filled with water that doesn't come. And it can't be addressed by technological solutions such as desalination, which can provide only marginal supplies of fresh water, and then only at enormous expense.
Please continue reading from source at:http://www.latimes.com/business/hiltzik/la-fi-hiltzik-20140620-column.html#page=1
Jun 23, 2014
Fracking Waste Ban is About Prudence, Not Protectionism via @BillSimmonsNJ
On May 12, 2014 the Senate passed the Fracking Waste Ban bill (S1041/A2108), 32 to 5. Now it's the NJ Assembly's turn to vote for banning the “treatment, discharge, disposal, or storage of wastewater, wastewater solids, sludge, drill cuttings or other byproducts from natural gas exploration or production using hydraulic fracturing.”
This is the second time around for NJ - the Senate and Assembly both passed a similar bill in 2012. But Governor Christie vetoed A575 over concerns that it was unconstitutional and favored in-state interests at the expense of out-of-state interests - economic protectionism.
With decades of hard-earned environmental regulations on the books for hazardous waste, why is a ban even needed?
Because fracking waste is not regulated like other potentially hazardous waste. The waste from fracking is exempt from the Clean Water Act, the Safe Drinking Water Act, the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act, and the Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act - commonly known as Superfund. The best-known exemption is the "Halliburton Loophole," which allows oil and gas operations toinject brine and other unregulated fracking fluids into or near drinking water aquifers.
Prudence
The lack of federal regulations means the safe disposal of fracking waste is decided state by state. Plus, some of the hundreds ofchemicals used in fracking are even protected as trade secrets. It's a black box.
But that doesn't mean fracking waste can't contaminate streams, groundwater, sediments, or leachate in solid waste landfills just like waste from regulated industrial operations. As first reported by Desmogblog on May 28th, the EPA found that tests of shale waste failed several standards: “drinking water maximum contaminant levels (MCLs) were exceeded for 8 parameters; water quality criteria for human health protection were exceeded for 9 parameters; and criteria for aquatic life protection were exceeded for 16 parameters.” The EPA found that fracking wastewater could “contain a wide variety of pollutants that may include total dissolved solids (TDS), chlorides, radionuclides, bromides, metals and organics.”
The exemptions only remove the hazardous characteristics of fracking waste on paper. That is why some sewage treatment plants and solid waste landfills in other states have been able to accept fracking waste without violating their NPDES permits. Public Works departments even started applying exempted fracking brine directly to roads as a de-icer.
If you make decisions assuming that exempted hazardous waste isn't really hazardous waste anymore, it's like turning the regulatory clock back 30-40 years.
Utah Utility Cuts Deal For 20 Years Of Solar Power Because It's The Cheapest Option
Boston-based renewable energy company First Wind just finalizedagreements to provide a Utah utility with 320 megawatts of solar capacity for the next two decades. And the circumstances of the contracts are yet another example of how falling solar prices are reshaping the market.
The agreement in this case is what's called a power purchase agreement(PPA), in which an energy provider (First Wind in this case) agrees to sell energy to a buyer (such as Utah utility Rocky Mountain) at a fixed payment rate for an agreed-upon amount of time. In other words, a PPA only makes market sense when an energy provider is confident they will be able to reliably generate the energy at a low cost for an extended period of time. In this case, the PPAs are a 20-year deal between First Wind and Rocky Mountain, for energy produced by four solar projects First Wind will build of 80 megawatts each.
That's a grand total of 320 megawatts of capacity, which should be able to produce over 800,000 megawatt-hours of energy annually — enough to power about 90,000 Utah homes. Construction is planned to begin in 2015, and end the next year.
"These additional long-term contracts with Rocky Mountain Power will enable us to move forward quickly with what will be the largest solar development in Utah, and our largest solar project to date," said First Wind CEO Paul Gaynor.
Please continue reading from source at:
Utah Utility Cuts Deal For 20 Years Of Solar Power Because It's The Cheapest Option | ThinkProgresshttp://thinkprogress.org/climate/2014/06/20/3451429/utah-solar-purpa/?elq=~~eloqua..type--emailfield..syntax--recipientid~~&elqCampaignId=~~eloqua..type--campaign..campaignid--0..fieldname--id~~
EPA’s McCarthy Says Carbon Emissions Rules rules are specifically designed to support nuclear plants that are struggling with profitability.
POWER Magazine: Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) head Gina McCarthy said on Tuesday that the agency's proposed carbon emissions rules are specifically designed to support nuclear plants that are struggling with profitability.
In Chicago to campaign for support from business leaders, McCarthy said the agency has focused on about 6% of the nation's nuclear fleet that is in danger of premature closure because of difficulties in competing with lower-cost gas-fired generation and subsidized renewables. The location for the remarks was significant because Chicago-based Exelon Corp., which operates the largest fleet of nuclear plants in the U.S., has said repeatedly that several of its plants may need to shut down on profitability concerns.
EPA's McCarthy Says Carbon Emissions Rules Will Boost Nuclear | POWER Magazinehttp://www.powermag.com/epas-mccarthy-says-carbon-emissions-rules-will-boost-nuclear/
Peak Coal: Why the Industry’s Dominance May Soon Be Over by Fred Pearce:
The coal industry has achieved stunning growth in the last decade, largely due to increased demand in China. But big changes in China's economy and its policies are expected to put an end to coal's big boom.
by fred pearce: After a decade in which coal has been grabbing an ever-larger share of the world's energy supply, could coal's boom be about to turn to bust? Both the United States and China are planning to curb coal, and analysts say the repercussions for the global industry could be dramatic. The world may soon breathe a great deal easier, as the biggest contributor to both urban smog and climate change goes into decline.
Earlier this month, the Obama administration announced curbs on CO2 emissions from coal-fired power plants, designed to deliver a cut in U.S.

Market analysts are suggesting that investors are about to pull the plug on coal. And as the coal tide retreats, the planet's vast investment in coal infrastructure could start to look as dumb as a subprime mortgage in 2007.
For all the talk of cutting emissions, coal's share of global energy use has risen in the last ten years.
This would be a huge turnaround. The rise in the past decade of coal, the most carbon-intensive of major fossil fuels, has been astounding. For all the political talk of cutting carbon emissions, coal's share of global energy rose from 25 to 30 percent. Most of this was due to China, which gets 80 percent of its electricity from coal.
As the world's largest energy user and CO2 emitter, China currently uses almost 50 percent of the world's coal. A staggering 82 percent of the global increase in coal use since 2000 has been attributable to China, according to the U.S. Energy Information Administration.
Having outstripped its own large coal reserves, China has been ransacking the world for coal, driving massive investments in new mining, notably in Australia, Indonesia, and Mongolia, but also in South Africa, Russia, and Kazakhstan. Its state-owned Shenhua Group is the world's largest coal company, almost twice the size of U.S. giant Peabody Energy. .
Please continue reading from source at:
Peak Coal: Why the Industry's Dominance May Soon Be Over by Fred Pearce: Yale Environment 360
http://environment360.yale.edu/feature/peak_coal_why_the_industrys_dominance_may_soon_be_over/2777/
The World Has 53.3 Years of Oil Left, and more peak oil news
BP (NYSE: BP ) has provided an intriguing update to its global oil reserves estimate in the company's latest yearly review of energy statistics. BP raised its reserve estimate by 1.1% to 1,687.9 billion barrels, which is enough oil to last the world 53.3 years at the current production rates. However, there's likely a lot more oil left in the tank beyond what BP sees today.
America's energy boom surges
A good portion of the growth in global oil reserves in BP's report comes from the United States. According to BP, the U.S. has 44.2 billion barrels of oil reserves, which is 26% higher than it previously thought. It's also quite a bit more optimistic than the U.S. Energy Information Administration, which recently increased its estimate to 33.4 billion barrels of reserves, or 15% more than previously thought.
The overall cause for that surge in oil reserves is that America's shale oil plays -- the Bakken, Eagle Ford and Permian Basin -- are now being unlocked through horizontal drilling technology.
Despite the big boost in reserves over the past year, there appears to be much more oil potential in each shale play, with the Permian Basin really standing out.

Source: Pioneer Natural Resources Investor Presentation.
As that slide points out, Pioneer Natural Resources (NYSE: PXD ) now estimates the Spraberry/Wolfcamp shale formations in the Permian Basin contain 75 billion barrels of recoverable oil and gas. That number is actually a major upward revision from last year when Pioneer estimated the two formations held 50 billion barrels of recoverable oil and gas.
These Permian Basin plays now make the Eagle Ford and Bakken shales look small in comparison. Yet the recoverable reserve estimates of both of those shale plays also continue to grow. In the four years since EOG Resources (NYSE: EOG ) began developing the Eagle Ford shale it has drastically revised its reserve estimates. The company now believes it will recover 3.2 billion barrels of oil equivalent on its land position, which is up from less than 1 billion barrels in 2010. New technologies and techniques, including closer spacing of wells, are providing a big boost to future reserve estimates.

Please continue reading from source at:
http://www.fool.com/investing/general/2014/06/22/the-world-has-533-years-of-oil-left.aspx
Garbage house, first permanent building built from waste and recycled materials.

Can garbage be used as an eco-material to construct a house? That's the intriguing premise behind the recently-completed Waste House project, which is believed by those involved to be the first permanent British building built almost solely from waste and recycled materials. Constructed at the University of Brighton's Grand Parade campus, the Waste House is an ongoing experiment which aims to prove, in the organizer's own words, that "there is no such thing as waste, just stuff in the wrong place." .. Continue Reading via Gizmag Emerging Technology Magazine
Jun 22, 2014
Buying Into Solar Power, No Roof Access Needed, community solar garden that is under development in state
NYTimes.com : Like many consumers, David Polstein had already done much to reduce energy use in his large Victorian home in Newton, Mass. He replaced his appliances with energy-efficient models, installed better heating and put in new insulation. But he was unable to get a solar system to reduce his utility bill, he said, because his roof is too small and shady to make it worthwhile.
Now, that could be changing. Mr. Polstein is considering joining a so-called community solar garden that is under development in his part of the state, one of many similar new arrangements now available in Massachusetts. Through the approach — largely pioneered in Colorado and spreading across the country — customers buy into a solar array constructed elsewhere and receive credit on their electricity bills for the power their panels produce.
For developers, such shared or community solar arrays create a new market from the estimated 85 percent of residential customers who can neither own nor lease systems because their roofs are physically unsuitable for solar or because they do not control them — like renters and people living in large apartment buildings. And for those customers, it offers a way into the solar boom, whether they seek to contribute to the spread of clean energy or to reap the potential cost savings.
"I pretty much realize that if I'm going to do this sort of thing," Mr. Polstein, a violin maker, said, "this is the only way I'm going to be able to do it."
Please continue reading from source at:
Buying Into Solar Power, No Roof Access Needed - NYTimes.com
http://www.nytimes.com/2014/06/20/business/energy-environment/buying-into-solar-power-no-roof-access-needed.html
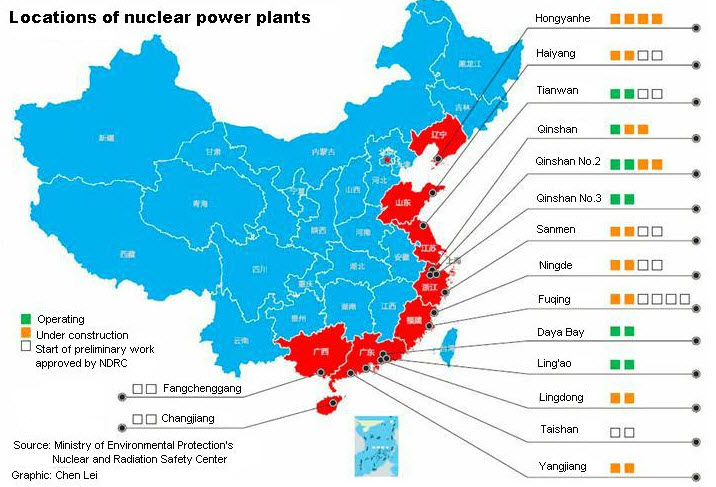
China Builds World's Most Powerful Nuclear Reactor; Regulators "Overwhelmed" via @ZeroHedge
(ZeroHedge, June 22, 2014): We are sure this will end well. Just as China took the 'if we build it (on free credit), they will come' growth model to extremes in real estate; it appears their ambitions in nuclear energy production are just as grandiose. However, just as they lost control of the real estate market, Bloomberg reports China is moving quickly to become the first country to operate the world's most powerful atomic reactor even as France's nuclear regulator says communication and cooperation on safety measures with its Chinese counterparts are lacking. France has a lot riding on a smooth roll out of China's European Pressurized Reactors (EPRs) as it is home to Areva, which developed the next-gen reactor, and utility EdF, which oversees the project. French regulators, speaking in parliament, warned, "the Chinese safety authorities lack means. They are overwhelmed."
Not what you want to hear as the nation embarks on the biggest nuclear energy facility creation ever, "if too many nuclear power projects are started too quickly, it could jeopardize the healthy, long-term development of nuclear power…" and the Chinese (just ask the Japanese).
As Bloomberg reports, China is moving quickly to become the first country to operate the world's most powerful atomic reactor even as France's nuclear regulator says communication and cooperation on safety measures with its Chinese counterparts are lacking.
http://www.zerohedge.com/news/2014-06-22/china-builds-worlds-most-powerful-nuclear-reactors-regulators-overwhelmed
US Government Introduces Pollinator Action Plan To Save Honey Bees
Please continue reading from source at:
US Government Introduces Pollinator Action Plan To Save Honey Bees
// b Slashdot
Startup Can Power Trillions of Sensors in Everyday Objects with vibration energy scavenging instead of batteries
Technology conceived at the University of Vermont could bring the sensor-driven IoT world closer to reality by helping overcome its Achilles' heel: how all those sensors will be powered, given the impracticality and expense of installing and changing batteries.
A tiny vibration energy scavenging device half the size of a sugar cube could replace the need for batteries.
"The market for wireless sensors is finally taking off, and their power requirements have dropped to the point where a good vibrational energy scavenger is plenty," Pister says. "And it looks like MicroGen has built a very good vibrational energy scavenger. It's an exciting time for the company."
Please read more from source:
WaterWars In #Detroit: Water For Corporations, Not For People | #water denied to families
Detroit citizens have been protesting the decision on the basis that water is a human right that cannot be denied to families who need it for cooking, bathing and flushing toilets. Many residents facing water shutoffs are currently on monthly payment plans with the Detroit Water and Sewerage Department, paying upwards of $160 per month as water rates continue to rise, and were given no prior notice that their water was about to be cut off. Last week, the Detroit City Council held a public hearing to discuss a proposed 4 percent hike in water rates.
As the Michigan Citizen reported, residents with delinquent water bills are losing their water while prominent Detroit corporations with much larger delinquent water bills are being left alone. The Palmer Park Golf Club owes $200,000. Joe Louis Arena, home of the Detroit Red Wings, owes DWSD $80,000. Ford Field owes $55,000. Kevyn Orr is arguing that the shutoffs are necessary to pay for the DWSD infrastructure – yet when Detroit raised $1 billion in bonds to pay for new infrastructure, $537 million of it went to banks like JPMorgan Chase, UBS and Morgan Stanley to pay off interest instead.
Community activists are placing blame on the structural, institutionalized poverty in Detroit that forces the people to foot the bill for corporate mismanagement. Detroit's bankruptcy and urban blight is a direct result of the housing bubble that burst, putting over 60,000 homes in foreclosure and rendering thousands of families homeless.
Please read full and follow at:
http://www.popularresistance.org/apartheid-in-detroit-water-for-corporations-not-for-people/
Jun 21, 2014
Video: World's first industrial-scale waste-to-biofuels facility

Thanks to its extensive composting and recycling facilities, the city of Edmonton, Canada is already diverting approximately 60 percent of its municipal waste from the landfill. That figure is expected to rise to 90 percent, however, once the city's new Waste-to-Biofuels and Chemicals Facility starts converting garbage (that can't be composted or recycled) into methanol and ethanol. It's the world's first such plant to operate on an industrial scale, and we recently got a guided tour of the place.
USA TODAY: Ebola virus broken through all containment barriers, called 'totally out of control' in West Africa
Earlier this year it was reported that the deadly Ebola virus had broken through all containment barriers making its way to seven west African countries. In an effort to stop widespread panic gripping the affected nations government officials told the Reuters news service that they would no longer release infection rates and death tolls to the public. In recent months, with no updates being provided to the public, many outside of Africa assumed that the virus spread had subsided.
But according to the latest figures the Ebola contagion is now deadlier than ever. A senior official with the organization Doctors Without Borders spoke with the Associated Press this week and warned that a second wave of the epidemic has taken hold, thus far claiming the lives of over 300 people with the infection confirmed in at least 550 people.
The Ebola outbreak ravaging West Africa is "totally out of control," according to a senior official for Doctors Without Borders, who says the medical group is stretched to the limit in its capacity to respond.
…
"The reality is clear that the epidemic is now in a second wave," Janssens said. "And, for me, it is totally out of control."
The outbreak, which began in Guinea either late last year or early this year, had appeared to slow before picking up pace again in recent weeks, including spreading to the Liberian capital for the first time.
"This is the highest outbreak on record and has the highest number of deaths, so this is unprecedented so far," said Armand Sprecher, a public health specialist with Doctors Without Borders.
Please read full and follow at: http://www.usatoday.com/story/news/world/2014/06/20/africa-ebola-outbreak/11110943/
Continuous System For Converting Waste Plastics Into Crude Oil from the 2 trillion tons of plastic waste is sitting in U.S. landfills
Continuous System For Converting Waste Plastics Into Crude Oil
// b Slashdot
Jun 20, 2014
Thyroid Cancer Rates Among Fukushima’s Children Skyrocket 40 Times Higher Than Normal
It's been almost 40 months since the Fukushima disaster and many want to pretend it never happened, but Fukushima's children are dying, thanks to thyroid cancer rates that are soaring to 40 times the normal rate since the nuclear meltdown.
This isn't a phenomenon affecting just a handful of children either. 48 percent of some 375,000 young people—nearly 200,000 kids—tested by the Fukushima Medical University near the smoldering reactors now suffer from pre-cancerous thyroid abnormalities, primarily nodules and cysts.

Please continue reading from source at:
The Coming Water Crisis That Will Change The Lives Of Every Person On The Planet
At this point, approximately 40 percent of the entire population of the planet has little or no access to clean water, and it is being projected that by 2025 two-thirds of humanity will live in "water-stressed" areas.
Today, the most important underground water source in America, the Ogallala Aquifer, is rapidly running dry. The most important lake in the western United States, Lake Mead, is rapidly running dry. The most important river in the western United States, the Colorado River, is rapidly running dry.
The U.S. intelligence community understands what is happening. According to one shocking government report that was released last year, the global need for water will exceed the global supply of water by 40 percent by the year 2030...
This sobering message emerges from the first U.S. Intelligence Community Assessment of Global Water Security. The document predicts that by 2030 humanity's "annual global water requirements" will exceed "current sustainable water supplies" by forty percent.Most Americans tend to think of a "water crisis" as something that happens in very dry places such as Africa or the Middle East, but the truth is that almost the entire western half of the United States is historically a very dry place. The western U.S. has been hit very hard by drought in recent years, and many communities are on the verge of having to make some very hard decisions.
For example, just look at what is happening to Lake Mead. Scientists are projecting that Lake Mead has a 50 percent chance of running dry by the year 2025. If that happens, it will mean the end of Las Vegas as we know it. But the problems will not be limited just to Las Vegas. The truth is that if Lake Mead runs dry, it will be a major disaster for that entire region of the country....
We are also depleting our groundwater at a very frightening pace as a recent Science Daily article discussed...
Three results of the new study are particularly striking: First, during the most recent drought in California's Central Valley, from 2006 to 2009, farmers in the south depleted enough groundwater to fill the nation's largest human-made reservoir, Lake Mead near Las Vegas -- a level of groundwater depletion that is unsustainable at current recharge rates.
Second, a third of the groundwater depletion in the High Plains occurs in just 4% of the land area. And third, the researchers project that if current trends continue some parts of the southern High Plains that currently support irrigated agriculture, mostly in the Texas Panhandle and western Kansas, will be unable to do so within a few decades.In the United States we have massive underground aquifers that have allowed our nation to be the breadbasket of the world. But once the water from those aquifers is gone, it is gone for good. That is why what is happening to the Ogallala Aquifer is so alarming..
The following are some facts about the growing water crisis that we are facing:
The Ogallala Aquifer is being drained at a rate of approximately 800 gallons per minute.
According to the U.S. Geological Survey, "a volume equivalent to two-thirds of the water in Lake Erie" has been permanently drained from the Ogallala Aquifer since 1940.
Scientists are warning that nothing can be done to stop the depletion of the Ogallala Aquifer...
According to the U.S. National Academy of Sciences, the U.S. interior west is now the driest that it has been in 500 years....
Right now, the United States uses approximately 148 trillion gallonsof fresh water a year, and there is no way that is sustainable in the long run.
According to a U.S. government report, 36 states are already facing water shortages or will be facing water shortages within the next few years.
It has been estimated that the state of California only has a 20 year supply of fresh water left.
It has been estimated that the state of New Mexico only has a 10 year supply of fresh water left.
Today, there are 1.6 billion people that live in areas of the globe that are considered to be "water-stressed", and it is being projected that two-thirds of the entire population of the globe will be experiencing "water-stressed" conditions by the year 2025.
It is being projected that the demand for water in China will exceed the supply by 25 percent by the year 2030.
http://www.activistpost.com/2013/03/30-facts-about-coming-water-crisis-that.html