Despite falling emission levels and reductions of some air pollutant concentrations over the past decades, EU air pollution is still far from being solved, according to the report, 'Air quality in Europe — 2013'.
Oct 31, 2013
Air quality still not good in European cities 90% exposed to unsafe levels of health damaging pollutants,
#Sustainable #LEED #Green Building is Now the Law in Dallas
Dallas has now accepted the first building permit applications under its green building ordinance. Dallas is one of the first major cities in the nation to implement comprehensive mandatory green building standards for both all new residential and commercial construction.
By Resolution 08-1070 adopted unanimously on April 9, 2008 Phase 1 of the law was effective in 2009 and Phase 2 (originally to be effective October 1, 2011) was fully implemented October 1, 2013.
All new projects must either: meet the minimum requirements of the Dallas Green Construction Code or be LEED certifiable or be Green Built Texas certifiable or be certifiable under an equivalent green building standard. Projects need only be "certifiable" and not LEED certified nor Green Built Texas certified.
Expedited review is available for projects that are at a minimum Dallas Green Construction Code compliant, LEED Silver certifiable or ASHRAE 189.1-2011 certifiable.
Projects must reduce water usage by 20%. LEED projects may achieve 1 point under the Water Use Reduction (20% Reduction) Credit or projects may use 20% less water than the baseline under the Plumbing Code.
Single family residential may also meet the minimum requirements of ICC 700. Lots must be designed so that at least 70% of the built environment is permeable. Projects must utilize drip irrigation for all "bedding areas" of landscaping.
Significantly, as one of the optional compliance paths a project may comply with the Dallas Green Construction Code, which is an enactment of the International Green Construction Code with local amendments. Many have noted Dallas deleted Chapter 6 of the IgCC, the energy conservation provision, and elected instead to keep existing energy code requirements. Also deleted are the chapters for commissioning and causing the code to apply to alterations of existing buildings.
Dallas also accepts approved third party plan review and inspection for its green building program.
The successful implementation of green building standards in Dallas has been widely heralded across the environmental industrial complex, including on the USGBC website. Although there are some minor rumblings that LEED certifiable versus actually submitting a project for LEED certification violates the terms of usage of the USGBC rating system.
Continue reading at ENN affiliate, Clean Techies.
Oct 30, 2013
U.S. Will Not Provide Financing For New International Coal-Fired Power Plants
Read more of this story at Slashdot.
People Who Live Downwind Of Alberta's Oil And #TarSands Operations Are Getting Blood #Cancer
Think Progress: A new study has found that levels of air pollution downwind of the largest tar sands, oil and gas producing region in Canada rival levels found in the world's most polluted cities. And that pollution isn't just dirtying the air — it also could be tied increased incidence of blood cancers in men that live in the area.
The study, published last week by researchers from University of California Irvine and the University of Michigan, found levels of carcinogenic air pollutants 1,3-butadiene and benzene spiked in the Fort Saskatchewan area, which is downwind of the oil and tar sands-rich "Industrial Heartland" of Alberta. Airborne levels of 1,3-butadiene were 322 times greater downwind of the Industrial Heartland — which houses more than 40 major chemical, petrochemical and oil and gas facilities — than upwind, while downwind levels of benzene were 51 times greater. Levels of some volatile organic compounds — which, depending on the compound, have been linked to liver, kidney and central nervous system damage as well as cancer — were 6,000 times higher than normal. The area saw concentrations of some chemicals that were higher than levels in Mexico City during the 1990s, when it was the most polluted city on the planet.
#Google could have another floating wage #energy data center in Maine, too
As CNET reported Friday, it looks very much like Google has been building a floating data center made from shipping containers on a barge in the middle of San Francisco Bay. But it may not be the only one of its kind.
Google has not responded to multiple requests for comment. But the project in San Francisco Bay appears likely to be the manifestation of a 2009 patent for a "water-based data center," and would likely leverage the fact that wave energy can provide cheap and plentiful power.
Now it seems as though Google may well have built a sister version of the project, and, according to the Portland Press Herald, it recently showed up in the harbor in Portland, Maine.
In both cases, the structures on both barges appear to be made from a number of shipping containers, many of which have small slats for windows, and each has one container that slants down to ground level at a 45-degree angle.
EPA proposes revised steam electric power regulations - via @WaterWorldMag
Over the last century, steam electric power has become a predominant source of energy for a number of municipal and industrial applications in the United States and across the globe. It relies heavily on the use of both nuclear matter and fossil fuels to generate electricity and meets around 82 percent of the nation's energy needs, according to the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA).

However, this conventional form of power often produces wastewater effluent with high levels of contaminants, including metals and nutrients such as mercury, lead, zinc, nitrogen and phosphorus, aluminum, manganese, and 30 other similar pollutants, according to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Further, EPA reports that "steam electric power plants contribute over half of all toxic pollutants discharged to surface waters by all industrial categories currently regulated in the United States under the Clean Water Act."
These contaminants have significantly contributed to a wide range of damaging effects to both public health and the environment, including a rise in cancer and neurological disorders, as well as harm to wildlife and aquatic life. Likewise, the EPA indicates that more than 160 waterbodies across the country are failing to meet state standards; roughly 185 have also been put under fish consumption advisories, and close to 400 potable water supply sources have been degraded as a result of uncontrolled steam electric power wastewater discharges.
To address these challenges, the EPA has proposed revised technology-based effluent regulations for the Steam Electric Power Generating category (40 CFR Part 423). The new rule aims to better control and strengthen primary waste streams at approximately 1,100 steam power plants across the U.S. to minimize wastewater discharges. The ruling would concentrate on available technologies that can replace or retrofit existing infrastructure.
In a free webinar hosted by the EPA in August to outline the organization's directive, Ron Jordan, project manager for the ruling, explained that "these technology-driven limits are intended to create a uniform set of requirements that are based on demonstrated technologies and processes."
Oct 29, 2013
Report puts pressure on animal agriculture and Congress to do something about issue of antibiotics
Henneberger writes about a report by the Johns Hopkins Center for a Livable Future. Its director, Bob Martin, said studies "show that as much as 80 percent of the antibiotics sold in this country are fed to food animals," Henneberger writes. "The more a particular germ is exposed to antibiotics, the more rapidly it can develop resistance. Most scientists agree that over-prescribing the drugs to humans is the predominant cause for bacteria evolving to outsmart them. Feeding the drugs widely to control and prevent disease in cows, pigs and chickens also is believed to play a role."
Shelly Burgess, a spokeswoman for the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, told the Post in an email that their plan to address the issue "is to phase out the use of medically important antibiotics in food animals for growth promotion and feed efficiency. FDA believes these drugs should be used only in situations where they are necessary for treating, controlling or preventing a specifically identified disease—and only under the oversight of a veterinarian." (Read more)
Canadian #Solar #Energy sees global solar installs at 100 GW per year
The head of Canadian Solar, one of the four biggest solar PV manufacturers in the world, expects the global installation rate of solar PV to treble by the end of the decade to more 100GW a year.In an interview with RenewEconomy, Shawn Qu, the CEO of Canadian Solar, said the declining costs of solar, and the rising cost of fossil fuels meant that the future of solar was guaranteed, although he had doubts about the future of large-scale centralised grid.
In 2012, the world installed more than 35GW of solar PV, which is expected to increase to around 40GW in 2013. Qu says that in two to three years, he expects to see a 50GW annual run rate, before rising to 100GW a year.
Ex-Chemical Firm Exec Gets Prison For Worker Death
Remember When Big Tobacco Sold Asbestos as the "Greatest Health Protection"?
It's hard to think of anything more reckless than adding a deadly carcinogen to a product that already causes cancer—and then bragging about the health benefits. Yet that's precisely what Lorillard Tobacco did 60 years ago when it introduced Kent cigarettes, whose patented 'Micronite" filter contained a particularly virulent form of asbestos.
Smokers puffed their way through 13 billion Kents between March 1952 and May 1956, when Lorillard changed the filter design. Six decades later, the legal fallout continues—just last month, a Florida jury awarded more than $3.5 million in damages to a former Kent smoker stricken with mesothelioma, an extremely rare and deadly asbestos-related cancer that typically shows up decades after the initial exposures.
Lorillard and Hollingsworth & Vose, the company that supplied the asbestos filter material, face numerous claims from mesothelioma sufferers, both factory workers who produced the cigarettes or filter material and former smokers who say they inhaled the microscopic fibers. (The companies insist that hardly any fibers escaped.) There's been a burst of new lawsuits in the last few years, according to SEC filings, possibly because a mesothelioma patient these days is almost certain to be asked by his doctor or lawyer, "Did you happen to smoke Kents in the 1950s?"
FDA issues proposed rule to help ensure the safety of food for animals
FDA issues proposed rule to help ensure the safety of food for animals
Source: U.S. Food and Drug Administration
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration today issued a proposed rule under the FDA Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA) aimed at improving the safety of food for animals. This proposed regulation would help prevent foodborne illness in both animals and people and is open for public comments for 120 days. The proposal is part of the Food Safety Modernization Act's larger effort to modernize the food safety system for the 21st century and focus public and private efforts on preventing food safety problems, rather than relying primarily on responding to problems after the fact.
The proposed rule would require makers of animal feed and pet food to be sold in the U.S.to develop a formal plan and put into place procedures to prevent foodborne illness. The rule would also require them to have plans for correcting any problems that arise. The proposed rule would also require animal food facilities to, for the first time, follow proposed current good manufacturing practices that address areas such as sanitation.
Oct 28, 2013
Electric Utility Executives Worry About #Solar #Energy Panels threat to a multibillion-dollar industry.
Aqualibrium Home #aquaponics kits, uses fish to grow plants, and plants to grow fish

Wristify thermoelectric bracelet makes heating and cooling personal [feedly]

CRS — Renewable Energy and Energy Efficiency Incentives: A Summary of Federal Programs
Renewable Energy and Energy Efficiency Incentives: A Summary of Federal Programs (PDF)
Source: Congressional Research Service (via Federation of American Scientists)
Energy is crucial to the operation of a modern industrial and services economy. Recently, there have been growing concerns about the availability and cost of energy and about environmental impacts of fossil energy use. Those concerns have rekindled interest in energy efficiency, energy conservation, and the development and commercialization of renewable energy technologies.
Many of the existing energy efficiency and renewable energy programs have authorizations tracing back to the 1970s. Many of the programs have been reauthorized and redesigned repeatedly to meet changing economic factors. The programs apply broadly to sectors ranging from industry to academia, and from state and local governments to rural communities. Since 2005, Congress has enacted several major energy laws: the Energy Policy Act of 2005 (EPACT 2005; P.L. 109-58); the Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 (EISA; P.L. 110- 140); the Energy Improvement and Extension Act (EIEA), enacted as Division B of the Emergency Economic Stabilization Act (EESA; P.L. 110-343); and the American Reinvestment and Recovery Act (ARRA; P.L. 111-5). Each of those laws established, expanded, or modified energy efficiency and renewable energy research, development, demonstration, and deployment (RDD&D) programs. The Department of Energy (DOE) operates the greatest number of efficiency and renewable energy incentive programs. The Department of the Treasury and the Department of Agriculture (USDA) operate several programs. A few programs can also be found among the Departments of Interior (DOI), Labor (DOL), Housing and Urban Development (HUD), Veterans Affairs (VA), and the Small Business Administration (SBA).
This report describes federal programs that provide grants, loans, loan guarantees, and other direct or indirect incentives for energy efficiency, energy conservation, and renewable energy. For each program, the report provides the administering agency, authorizing statute(s), annual funding, and the program expiration date. The appendixes provide summary information in a tabular format and also list recently expired programs.
Another Trillion in Debt. New debt under the 8 years of the Obama administration than we did under all of the other presidents in U.S. history combined.
Over the past five years, the U.S. government has been on the greatest debt binge in history. Unfortunately, most Americans don't realize just how bad things have gotten because the true budget deficit numbers are not reported on the news. The following is where the U.S. national debt has been on September 30th during the five years previous to this one...
09/30/2012: $16,066,241,407,385.89
09/30/2011: $14,790,340,328,557.15
09/30/2010: $13,561,623,030,891.79
09/30/2009: $ 11,909,829,003,511.75
09/30/2008: $10,024,724,896,912.49
The U.S. national debt is now 37 times larger than it was 40 years ago, and we are on pace to accumulate more new debt under the 8 years of the Obama administration than we did under all of the other presidents in U.S. history combined.
Of course all of the blame can't be placed at the feet of Obama. During the last two elections the American people have given the Republicans a solid majority in the U.S. House of Representatives, and the government cannot spent a single penny without their approval.
Oct 27, 2013
Introduction to Persistent, Bioaccumulative, Toxic (PBT) Compounds in the Environment
ENN Original news: Global chemical contamination is a worldwide concern affecting every being on earth. Chemical exposure, whether it is through air, water, plants, soil or our modern living environment is unavoidable. But certain chemicals and compounds having Persistent, Bioaccumulative, Toxic (PBT) characteristics are more dangerous to our environment than others because of their inability to break down easily, are easily transferred throughout all forms of environmental media, and posing risks to human health and the ecosystem due to their toxicity at low concentrations.
Currently, the UN, EPA, and many other countries are working to identify and develop strategies to reduce these risks by inhibiting the transfer of those PBTs that are already present in our environment and preventing and limiting new PBTs from entering the environment either through commerce or waste residual.
The EPA has a list of 16 chemicals and 4 chemical categories for PBTs, which are subject to reporting. The UN has a similar list of which began with a list of twelve Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs) billed as the 'Dirty Dozen'. Both lists have evolved over time to reflect changing conditions. Although the EU is currently ahead of the US on this issue, amongst all countries involved, much is being done to identify, and consistently regulate the PBT use globally.
The EPA PBT list identifies the most dangerous chemicals, which were or are used: pesticides, petroleum derivatives (polyaromatic hydrocarbons [PAHs]), certain metals, PCBs, dioxins/furans, amongst others. These PBTs are found in numerous everyday products and residuals.
A PBT is capable of remaining in the environment in an unchanged form in air, water, soil, or sediment and is expressed in half-lives. Scientists studying PBTs are also concerned with the Bioconcentration within aquatic systems and Biomagnification within animals through their diets. Scientists will test for toxicity in fish and animals for chronic exposure and its subsequent adverse health effects.
Tools, such as the EPA PBT Profiler have been developed to predict if a substance is PBT.
The results of all of this testing is to protect human health and the environment. When a PBT is identified, it is important to limit its use by finding a substitution unless the manufacturer can demonstrate a very compelling socio-economic benefit that would outweigh the risk.
Read more at the EPA and the UNEP.
Additional support for this article came from Laurie Gneiding of AMEC (laurie.gneiding@amec.com).
The CDC has released a first-of-its-kind report detailing the threat of antibiotic-resistant bacteria to our health and food supply. It is not pretty.
Thousands of people are killed by such infections every year. They inflict billions of dollars of medical costs and lost wages. The drug-development pipeline for new antibiotics is almost empty. New tools like fecal transplants and phage therapy are hopeful but still experimental, and at least a decade away. So what do we do?
The CDC calls for safer use of antibiotics, both in hospitals and on farms, and increased screening and vaccination efforts. CDC director Tom Frieden put it plainly:
"If we are not careful, we will soon be in a post-antibiotic era."
Unless we do something to reverse this trend, and fast, it's high time to tuck your head between your knees. We're either on a plane that's going down, or we're about to get paddled. The choice of metaphors is yours.
It's important that people are educated on the grave nature of this threat, because it is very serious. Make sure your doctors are informed and are prescribing antibiotics correctly, hold your elected officials accountable for safer food and farm policies … and for the budding biologists out there, we've got plenty of new problems for you to solve. We're gonna need your help.
Oct 26, 2013
Dead battery troubles will soon be a thing of the past
ENN Original news:,Current technology is limited in regards to battery life. Not only does it affect our personal devices, but the lack of energy storage is also a critical issue in the energy sector, especially wind farms and solar power plants. Currently, there is no affordable, long-life battery that stores large amounts of energy for those overcast days or windless afternoons. Today's batteries are expensive, have problems with heat output, limited lifespans, and are toxic or corrosive.
However, a new prototype is in the works at start-up company lead by Amy Prieto, a chemist at Colorado State University. The company is working on developing an energy storage device that combats these major issues, with the addition of being more environmentally friendly than standard batteries. The battery is based around a copper foam structure, which serves as the current collector on the anode side of the battery. The foam has a 3D structure that increases the surface area of the electrodes and brings them closer together, which in turn increases the power density of the battery. According to Prieto, "In terms of energy density, the foam should also get more bang for the buck. The intricate 3D structures utilize the electrode material more efficiently than a flat surface."
The team also uses electroplating equipment made from copper antimonide, which is inexpensive compared to the equipment needed to make other types of batteries.
The team has calculated that the foam battery should store the same amount of energy as conventional batteries in two-thirds the volume, charge five to ten times faster, and last up to ten times longer.
Less than one year away from completing the prototype, the team already plans on testing the foam battery on electric bikes and portable electronics. "This was my personal dream," says Prieto. "I didn't think it would actually work, but it now looks like it will."
The above article is based on materials provided by American Institute of Physics, via Eurekalert.
A 140-Acre Urban Forest Is About to Materialize in the Middle of Detroit
After nearly five years of planning, a large-scale attempt to turn a big chunk of Detroit into an urban forest is now underway. The purchase of more than 1,500 vacant city-owned lots on the city's lower east side – a total of more than 140 acres – got final approval from Detroit Emergency Manager Kevyn Orr and Michigan Governor Rick Snyder last week.
The buyer is Hantz Farms, and it's a venture of financier John Hantz, who lives in the nearby Indian Village neighborhood. Indian Village is an affluent enclave of manor-scale historic homes, but much of the surrounding area is blighted. Hantz Farms will pay more than $500,000 for the land, which consists of non-contiguous parcels in an area where occupied homes are increasingly surrounding by abandoned properties.
The company has committed to clearing 50 derelict structures, cleaning up the garbage dumped across the neighborhood, planting 15,000 trees, and mowing regularly. Planting of the hardwoods will begin in earnest next fall, and the urban forest will be called Hantz Woodlands.

The area that will become the Hantz Woodlands. Photo by Joseph Murphy/Bassett & Bassett
The huge deal drew criticism last year, when the city council – which was then still in control of Detroit – voted 5-4 to approve the sale. A coalition of grassroots urban farmers and community activists opposed it, charging that it was a play to increase land values by buying a huge swath of acreage and taking it off the market. "I think it opens the gateway for other rich folks to come here to buy up land and essentially make themselves rich compounds," urban gardener Kate Devlin told The Huffington Post at the time.
Oct 25, 2013
Fleet #energy #sustainability: Ford Fires Up Natural Gas Powered Pickups for $1 per gallon
Back in 2011, Jon Coleman was doing something he does just about every day in his job — talking to customers — when something piqued his interest. As the fleet sustainability and technology manager for Ford Motor Co. (NYSE: F), Coleman constantly tries to stay abreast of the wants and needs of those who run vehicle fleets: police forces, taxicab outfits and delivery companies. So he perked up when a big customer asked about compressed natural gas, or CNG. Specifically, the customer wanted 1,000 new natural gas powered vehicles. "When they say that, we take notice," Coleman says.
That customer has a lot of company these days. At the end of July, Ford announced that the 2014 Ford F-150 — the longtime best-selling vehicle in America — will be available with a 3.7-liter V-6 engine capable of running on CNG or standard petroleum gas. Coleman expects that initial sales of the CNG-prepped 2014 Ford F-150 — which can also include a separate fuel system that runs on standard gas — will mostly go to fleet customers. But as fueling stations offering CNG multiply across the country, he also expects interest among individual customers to grow too.
"Gas and diesel prices bounce all over the place, but CNG is a flat line, rising right along with inflation," says Coleman. And, he adds, prices have dropped precipitously in recent years due to increased drilling and new technologies. "Fleet customers are interested in that lack of volatility and the low price, which they can lock in through forward contracts," driving down the cost of ownership. At the time of their announcement about the F-150, Ford said CNG was selling for an average of $2.11 per gallon of gasoline equivalent and was as low as $1 in some parts of the country, while the national average for unleaded gas was $3.66 per gallon.
We’ve Reached “The End of Antibiotics, Period” | Hunting the Nightmare Bacteria | FRONTLINE
Via: NPR: What do you mean?
A lot of Gram-negative bacteria, they come out of the box, if you will, resistant to a number of important antibiotics that we might use to treat them. We're talking about agents with names like Acinetobacter, Pseudomonas, E. coli.
These are bacteria that have historically done a very good job of very quickly developing resistance to antibiotics. They have a lot of tricks up their sleeves for developing resistance to antibiotics, so they're a group of agents that can quickly become resistant, can pose major challenges to resistance.
And what we've seen over the past decade is these Gram-negative agents becoming very rapidly more and more resistant to all of the agents that we have available to treat them.
To all of the agents?
There are Gram-negative bacteria that have developed resistance to everything, for which we have no viable antibiotics left to treat them. …
So why are we so worried about these new bacteria that are Gram negatives, and what's happened recently?
…For a long time we've seen Gram negatives develop resistance to antibiotics, but we had other tricks up our sleeves. We had other antibiotics that we could use.
Increasingly, though, what we've seen is that they're developing resistance even to the agents that we've been sort of holding back and only using in the most serious infections. They were our last, best line of defense, and we now see some of these Gram-negative organisms that are resistant to even that last line of defense.
Oct 24, 2013
Urban #agriculture and #aquaponic spreading
Urban farmers have to think creatively to maximize space and fit their operations into the urban environment.
These examples from Food Tank illustrate the innovative forms of urban agriculture around the world.
1. Food Field, Detroit, MI
Food Field offers a Community Supported Agriculture (CSA) that provides nutritious food and economic opportunities for the neighborhood. Noah Link and Alex Bryan created Peck Produce in 2011 and converted the former site of an elementary school into a revitalized farm. Food Field produces food that the local community asks for, including farm favorites like salad greens and mulberries. Food Field is expanding with a new aquaponics system to raise fish, such as catfish and blue gill, in addition to collecting eggs from chickens and ducks.
2. FARM:shop and FARM:London, London, UK
The self-proclaimed first urban farming hub, FARM:shop offers the neighborhood small-scale farming, aquaponic fish farming, a rooftop chicken coop, workspaces and a café inside a former neglected storefront.
3. Sky Greens, Singapore
Sky Greens, the world's first low-carbon hydraulic water-driven urban vertical farm, reduces the amount of energy and land needed for traditional farming techniques. The vertical systems, which are three stories high and located within a greenhouse, produce five to 10 times more per unit area compared to conventional farms. The greenhouse and low-carbon hydraulic system grows lettuces and cabbages year-round using less energy and water.
4. The Distributed Urban Farming Initiative, Bryan, TX
Distributed Urban Farming Initiative builds gardens in otherwise empty spaces, prompts neighbors to eat healthy food, and drives entrepreneurship and tourism. This past winter, DUFI grew broccoli, cauliflower, cabbage and lettuce in a raised bed and pallet gardens.
5. Sharing Backyards, throughout Canada, U.S. and New Zealand
Sharing Backyards offers a solution for people who lack land but want to grow their own food locally by linking them with people who have unused yard space. Through a website, those with unused property can post their approximate location, while those looking for space to grow food locally can search locations nearby at no cost.
#Obamacare About to Skyrocket Your Health Care Costs: Wisconsin costs to jump by 80% or more.
I've heard this clever quip about health care reform many times before, but this quote by P.J. O'Rourke was supposed to prove meaningless thanks to the passing of the Affordable Care Act in 2010... right?
Crafted by President Obama and lawmakers, the ACA, also known in shorthand asObamacare, was to create a competitive pool of insurance companies competing for consumers' premium dollars which would help drive the costs of medical care and premiums lower. In addition to creating these pools, the ACA:
- Required insurers to spend at least 80% of patient premiums on care or return the difference.
- Would not allow insurers to turn away patients with pre-existing conditions.
- Would expand the existing pool of qualifying government-sponsored Medicaid patients.
- Would establish a medical device excise tax that would collect 2.3% of revenue from all medical device makers to help pay for the Medicaid expansion.
- Would mandate individuals to carry health insurance.
Sure, the SOA's report demonstrated strength in certain states, with five expected to see underlying claims costs drop. However, that means costs are expected to rise in the remaining 45 states, with 37 of those states expecting costs to jump by 20% or more. According to the SOA's report, Ohio and Wisconsin can expect their claims costs to jump by 80% or more.
Oct 23, 2013
Jerky treat mystery: Nearly 600 pets dead; still no source, FDA
WRCBtv.com: Nearly 600 pets have died and more than 3,600 have been sickened in an ongoing, mysterious outbreak of illnesses tied to jerky treats made in China, federal animal health officials said Tuesday.
Most of the cases have been in dogs of all breeds, ages, shapes and sizes, although 10 cats have been sickened, too. The pace of the reported illnesses appears to have slowed, but federal Food and Drug Administration officials are now seeking extra help from veterinarians and pet owners in solving the ongoing puzzle.
"To date, testing for contaminants in jerky treats has not revealed a cause for the illnesses," Martine Hartogensis, a deputy director for the FDA's Center for Veterinary Medicine, said in the new report. "Despite these warnings, we have continued to receive reports of illnesses in both cats and dogs."
The new numbers are up from some 500 deaths and 3,200 illnesses tallied in January, but the rate of reports has fallen sharply since then, mostly because two of the largest sellers of pet chicken jerky treats announced recalls tied to the presence of unapproved antibiotic residue detected in the products.
FDA officials don't think that antibiotic residue is the big problem that has stumped the agency since 2007, when pet owners started reporting their animals were suffering gastrointestinal and kidney problems after eating the popular jerky treats.
Instead, it's likely that the recall of Nestle Purina PetCare Co.'s Waggin Train and Canyon Creek Ranch treats, plus Del Monte Corp.'s Milo's Kitchen Chicken Jerky and Chicken Grillers home-style dog treats simply resulted in fewer treats being available. Two other smaller producers also recalled the treats because of the problem.
In fact, FDA officials remain as uncertain as ever about the source of the problem that has led to reports of illnesses and warnings about the possibility of Fanconi syndrome and other kidney problems in animals that ate jerky treats.
"We still are extensively testing treats for a number of things," Hartogensis told NBC News. "We do seem to be getting some leads, but we still have a little bit of a ways to go."
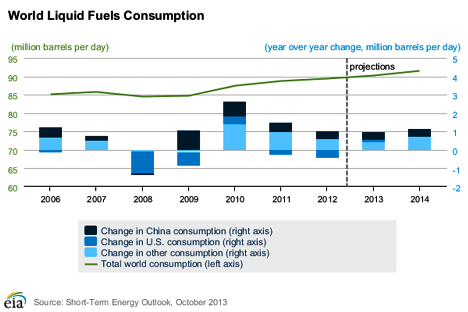
China is Now the World’s Largest Importer of Oil—What Next?
- China Is Now The World's Largest Importer Of Oil – What Next? (Oil Price, Oct 15, 2013):
Last month the world witnessed a paradigm shift: China surpassed the United States as the world's largest consumer of foreign oil, importing 6.3 million barrels per day compared to the United States' 6.24 million. This trend is likely to continue and this gap is likely to grow, according to the EIA's October short-term energy outlook. Wood Mackenzie, a leading global energy consultancy, echoed this prediction, estimating Chinese oil imports will rise to 9.2 million barrels per day (70% of total demand) by 2020.
This trend has been driven by a combination of factors. Booming American oil production, slow post-recovery growth, and increasing vehicle efficiency have all served to reduce crude imports. In China, however, continued economic growth has brought with it a growing middle class eager to take to the road. While the automobile market had cooled earlier this year, September saw sales rise by 21%—a trend that is putting increasing strain on China's infrastructure and air quality in addition to oil demand.
Some of the world's largest traffic jams are now commonplace in major Chinese cities, and air quality issues have pushed authorities to pursuesynthetic natural gas technology to offset the need for coal-fired electricity. Increasing oil consumption will only serve to exacerbate these issues.
Furthermore, the per capita consumption differential between the two countries is still vast, with an average Chinese citizen consuming a mere 2.9 barrels of oil per year compared to an average American who consumes 21.5. This indicates that China's growing thirst for oil isn't going to slow down anytime soon.
So what does this shift in oil imports mean?
Nuclear Engineer: Pyrophoric fire may have already occurred at Fukushima Unit 4 spent fuel pool — Explosion possibly due to rods not being covered with water
Title: Interview with Chris Harris
Source: Nutrimedical Report
Date: Oct. 17, 2013At 23:00 in
Chris Harris, former licensed Senior Reactor Operator and engineer: There's a website I was looking at about, remember we talked a lot about the FOIAs, Freedom of Information Act responses, that were asked from the media and from the alternative media, back in the time frame of April of 2011, and see what was really going on, a lot of those were released. There's a website named Hatrick Penry, I was looking at it this week, they just put out another blog, and I sent you a link to his website, what he did was he put a lot of those in order. Some of the things that we have done also, he had some good comments about it, I give credit where credit is due. And the pyrophoric fire on Unit 4 spent fuel pool, they may have actually had it. It's not conclusive what was the cause of the explosion on Unit 4, it's not conclusive where did the hydrogen come from, and would indicate that they did have uncovering of the fuel at one point. So there's a lot of evidence in those FOIAs and it's all strung together […]
Plug&Sun CPV system powers up remote Madagascan village

Oil and Chemical Spills: Federal Emergency Response Framework (PDF)
Oil and Chemical Spills: Federal Emergency Response Framework (PDF)
Source: Congressional Research Service (via Federation of American Scientists)
Thousands of oil and chemical spills of varying size occur in the United States each year. State and local officials located in proximity to these incidents generally are the first responders and may elevate an incident for federal attention if greater resources are desired. The National Oil and Hazardous Substances Pollution Contingency Plan, often referred to as the National Contingency Plan (NCP), establishes the procedures for the federal response to oil and chemical spills. The scope of the NCP encompasses discharges of oil into or upon U.S. waters and adjoining shorelines and releases of hazardous substances into the environment. Several hundred toxic chemicals and radionuclides are designated as hazardous substances under the NCP, and other pollutants and contaminants also may fall within the scope of its response authorities.
The Great Lakes Restoration Initiative: Background and Issues (PDF)
The Great Lakes Restoration Initiative: Background and Issues (PDF)
Source: Congressional Research Service (via National Agricultural Law Center)
The Great Lakes ecosystem is recognized by many as an international natural resource that has been altered by human activities and climate variabi lity. These alterations have led to degraded water quality, diminished habitat, lower native fish and wildlife populations, and an altered ecosystem. In response, the federal governments of the United States and Canada and the state and provincial governments in the Great Lakes basin are implementing several restoration activities. These activities range from mitigating th e harmful effects of toxic substances in lake waters to restoring fish habitat.
Most laws and efforts in the past addressed specific issues in the Great Lakes; a few addressed issues at the ecosystem level. This caused the Government Accountability Office and others to express the need for initiating and implementin g a comprehensive approach for restoring the Great Lakes ecosystem. In 2010, the Great Lakes Re storation Initiative (GLRI) was proposed and implemented by the Obama Administration. The aim of GLRI is to restore the Great Lakes ecosystem under one initiative. Specifically, the GLRI is to restore and maintain the chemical, physical and biological integrity of the Great Lakes Basin Ecosystem by directing activities to address five focus areas: (1) toxic substances and Areas of Concern (these are areas in the Great Lakes that are environmentally degraded); (2) invasive species; (3) nearshore health and nonpoint source pollution; (4) habitat and wildlife protection and restoration; and (5) accountability, monitoring, evaluation, communication, and partnerships.