Mar 20, 2018
Top Story OSHA Will Enforce Beryllium Standard Starting in May
What Is The USEPA Revised Hazardous Waste Generator Rule And How It Affects You
Preventing Illness from Pesticide Drift
As the breadbasket for the United States, California has many communities and workplaces surrounded by agriculture. Workers can become ill when pesticide drifts onto workplaces after it is applied incorrectly.
A new fact sheet and poster from the California Department of Public Health's Occupational Pesticide Illness Prevention Program (OPIPP) provides employers and workers with tips for preventing pesticide illness from drift incidents. The fact sheet will help workplaces located near pesticide applications to plan ahead and know who to contact to report drift. A case study illustrates the need to plan in advance and train workers on how to respond.
The companion poster reinforces what to do in a drift situation and provides an easy way to post the contact information for reporting drift.
You can find more information and resources about OPIPP on their website.
Email Occupational Health Watch with feedback about this update or change of address.
Resources
Plan Ahead to Prevent Pesticide Drift from Causing Illness – fact sheet
What to Do If Pesticides Drift onto Our Workplace – poster
Occupational Pesticide Illness Prevention Program website
Annual Death Toll From Opioid Epidemic Exceeds That of the Vietnam War
The opioid epidemic — which between 2002 and 2015 alone claimed an estimated 202,600 Americans' lives1 — shows absolutely no signs of leveling off or declining. On the contrary, recent statistics suggest the death toll is still trending upward, with more and more people abusing these powerful narcotics. The most common drugs involved in prescription opioid overdose deaths include2 methadone, oxycodone (such as OxyContin®) and hydrocodone (such as Vicodin®).
This dangerous class of drugs promises relief from pain and is filling a hole in human hearts and souls everywhere. According to the most recent data3 from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), overdose cases admitted into emergency rooms increased by more than 30 percent across the U.S. between July 2016 and September 2017. Overdose cases rose by:4
- 30 percent among men
- 31 percent among 24- to 35-year-olds
- 36 percent among 35- to 54-year-olds
- 32 percent among those 55 and older
In the Midwest region — Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Kansas, Michigan, Minnesota, Missouri, Nebraska, North Dakota, Ohio, South Dakota and Wisconsin — overdose cases rose by 70 percent and opioid-related mortality by 14 percent. Large cities also saw a 54 percent increase in overdose cases in that same timeframe. According to CDC officials, the results are "a wake-up call to the fast-moving opioid overdose epidemic.''
'The Opioid Diaries'
Curiously, opioid abuse appears to be a uniquely American problem. As noted in a recent write-up in New York Magazine,5 the U.S. "pioneered modern life. Now epic numbers of Americans are killing themselves with opioids to escape it." I've written about opioid misuse and addiction on many occasions in recent years, and it seems one cannot discuss this issue enough. Many are still unaware of the dangers involved with filling that first prescription.
As an indication of the need for awareness, the March 5 issue of Time magazine, "The Opioid Diaries,"6 is aimed at exposing the national crisis. For the first time in the magazine's history, an entire issue is devoted to a single photo essay — the work of photojournalist James Nachtwey, who has documented stories for Time for over three decades. In "The Opioid Diaries," Nachtwey's photos detail the stark reality of this all-American crisis.
He and editor Paul Moakley spent months traversing the U.S., interviewing over 200 people along the way. As noted by a deputy sheriff who has seen more than his fair share of the fallout of this epidemic, opioid addiction doesn't discriminate. "It's not just the guy who's never worked a day in his life," he says. "It's airline pilots. It's teachers. I'm sure there's law enforcement, firemen out there hooked on it. It's Joe Citizen that's dying."
A Country in Crisis
Here are some statistics about the U.S. opioid epidemic that really ought to get everyone's attention:
Leading cause of death for younger Americans Drug overdoses are now the leading cause of death among Americans under the age of 50.7 |
Annual death toll greater than entire Vietnam War Preliminary data for 2016 reveals the death toll from drug overdoses may be as high as 65,000,8 a 19 percent increase from 2015; the largest annual increase of drug overdose deaths in U.S. history, and a number that exceeds both the AIDS epidemic at its peak and the death toll of the Vietnam War in its entirety.9 That much-opposed war claimed the lives of 58,000 American troops. Now, we're suffering a death toll exceeding that of the Vietnam War each and every year, courtesy of a drug addiction epidemic created by the pharmaceutical industry. |
Deadlier than breast cancer Opioids, specifically, killed 33,000 in 2015,10,11,12 and 42,249 in 2016, which is over 1,000 more deaths than were caused by breast cancer that same year.13 |
Synthetic opioid abuse skyrocketing Deadly overdoses involving fentanyl, an incredibly potent synthetic opioid, rose by 50 percent between 2013 and 2014 and another 72 percent between 2014 and 2015. Over 20,000 of the drug overdose deaths in 2016 were attributed to fentanyl and other synthetic opioids.14 In Rhode Island, New Hampshire and Massachusetts, fentanyl was responsible for at least 70 percent of all opioid-related deaths between July and December 2016.15 While some users will buy fentanyl on purpose, others buy tainted wares and end up taking it without knowing the risks. This is a critical problem, as fentanyl is so potent just a few grains can be deadly. An inexpensive fentanyl test strip can check for the presence of the drug, and trials where test strips have been given to users show they're more likely to cut back on the amount they're taking when they know it's tainted with fentanyl. As such, fentanyl testing can be employed as "a point-of-care test within harm-reduction programs" aimed at lowering the death toll.16 |
Significant factor in unemployment rates Opioid abuse has been identified as a significant factor in rising unemployment among men, accounting for 20 percent of the increase in male unemployment between 1999 and 2015.17 Nearly half of all unemployed men between the ages of 25 and 54 are using opioids on a daily basis.18 |
Americans use vast majority of global opioid supplies Americans consume 99 percent of the hydrocodone sold worldwide, and 81 percent of all oxycodone — approximately 30 times more than medically necessary for the population size of the U.S.19 A number of different statistics convey this massive overuse. For example, in a five-year span, between 2007 and 2012, 780 million hydrocodone and oxycodone pills were shipped to West Virginia, which has just 1.8 million residents.20 More than 1 in 5 Americans insured by BlueCross BlueShield were prescribed an opioid in 2015, and insurance claims involving opioid dependence rose by nearly 500 percent between 2010 and 2016.21 |
Declining life expectancy Life expectancy for both men and women in the U.S. has declined two years in a row,22,23 and this decline is largely attributable to the opioid crisis. Just as the opioid epidemic, declining life expectancy is a uniquely American phenomenon. No other developed countries has experienced this decline in life expectancy. |
A Story of Misery
There are compelling reasons to suspect the opioid epidemic was purposely engineered by the drug companies that make them, and that these same companies have, and continue to, shy away from doing what's necessary to curb the use of opioid pain killers for financially-driven reasons.
Moreover, while this was not likely planned, the industry's misleading promotion of narcotic pain relievers appears to have coincided with a growing trend of emotional pain and spiritual disconnect, and opioids satisfy people's need not only for physical pain relief but also psychological and existential pain relief. As noted by New York Magazine:24
"The scale and darkness of this phenomenon is a sign of a civilization in a more acute crisis than we knew, a nation overwhelmed by a warp-speed, postindustrial world, a culture yearning to give up, indifferent to life and death, enraptured by withdrawal and nothingness …
[U]nless you understand what users get out of an illicit substance, it's impossible to understand its appeal, or why an epidemic takes off, or what purpose it is serving in so many people's lives. And it is significant, it seems to me, that the drugs now conquering America are downers: They are not the means to engage in life more vividly but to seek a respite from its ordeals … And some part of being free from all pain makes you indifferent to death itself."
The article cites a number of firsthand accounts of the experience opioids provides — the blissful serenity of being able to stand apart from one's psychological pain in addition to physical pain; the sensation of being connected to some deeper wellspring of peace. These are experiences typically derived from spiritual practices, and hint at a widespread lack of connectedness to the divine in general.
Mar 16, 2018
ECHA: New website about chemicals for consumers launched today
Mar 15, 2018
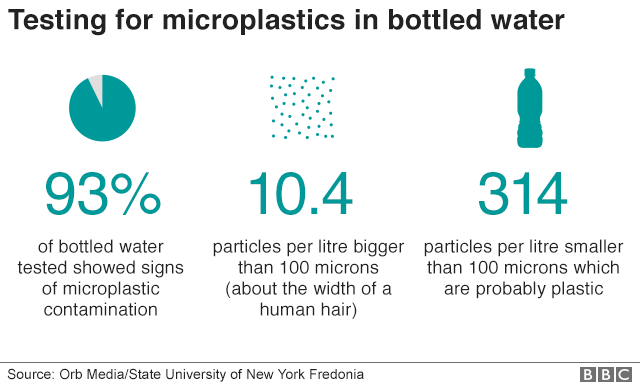
Study finds that 90% of bottled water contains tiny plastic particles
BBC News: Prof Mason and her colleagues filtered their dyed samples and then counted every piece larger than 100 microns – roughly the diameter of a human hair.
Some of these particles – large enough to be handled individually - were then analysed by infrared spectroscopy, confirmed as plastic and further identified as particular types of polymer.
Particles smaller than 100 microns – and down to a size of 6.5 microns – were much more numerous (an average of 314 per litre) and were counted using a technique developed in astronomy for totalling the number of stars in the night sky.
The make-up of these particles was not confirmed but Prof Mason said they can "rationally expected to be plastic".
This is because although Nile Red dye can bind to substances other than plastic - such as fragments of shell or algae containing lipids - these would be unlikely to be present in bottled water.
Since the study has not been through the usual process of peer review and publication in a scientific journal, the BBC has asked experts in the field to comment.
Dr Andrew Mayes, of the University of East Anglia and one of the pioneers of the Nile Red technique, told us it was "very high quality analytical chemistry" and that the results were "quite conservative".
Michael Walker, a consultant to the Office of the UK Government Chemist and founder board member of the Food Standards Agency, said the work was "well conducted" and that the use of Nile Red has "a very good pedigree".
Both of them emphasised that the particles below 100 microns had not been identified as plastic but said that since the alternatives would not be expected in bottled water, they could be described as "probably plastic".
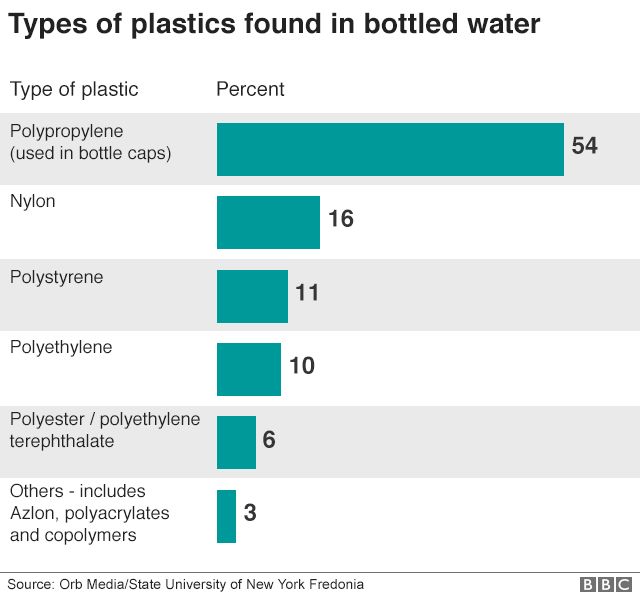
One obvious question is where this plastic may be coming from. Given the amount of polypropylene, which is used in bottle caps, one theory is that the act of opening a bottle may shed particles inside.


To check that the process of testing was not itself adding plastic to the bottles, Prof Mason ran "blanks" in which the purified water used to clean the glassware and the acetone used to dilute the Nile Red dye were themselves investigated.
Small quantities of plastic were found in them – believed to be from the air - but these were subtracted from the final results.
A surprise to researchers was the wide variety of findings – 17 of the 259 bottles tested showed no evidence of plastic but all of the rest did, with big differences even within brands.
Read on at: http://www.bbc.com/news/science-environment-43388870
Mar 14, 2018
EPA Proposes Universal Waste Designation for Aerosol Cans
(PAINT.ORG) The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is proposing to add hazardous waste aerosol cans to the universal waste program under the federal Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) regulations. In a pre-publication notice signed March 5 by EPA Administrator Scott Pruitt, the agency said, "this proposed change, once finalized, would benefit the wide variety of establishments generating and managing hazardous waste aerosol cans, including the retail sector, by providing a clear, protective system for managing discarded aerosol cans."
EPA will accept comments for the 60-day period following the official publication notice in the Federal Register.
The streamlined universal waste regulations are expected to ease regulatory burdens on retail stores and others that discard hazardous waste aerosol cans; promote the collection and recycling of these cans; and encourage the development of municipal and commercial programs to reduce the quantity of these wastes going to municipal solid waste landfills or combustors.
Under the proposed reclassification, aerosol cans, pressurized or spent — including spray paint cans — would be treated and handled as universal waste. In 1995, EPA promulgated the universal waste rule to establish a streamlined hazardous waste management system for widely generated hazardous wastes to encourage environmentally sound collection and proper management of the wastes within the system. Hazardous waste batteries, certain hazardous waste pesticides, mercury-containing equipment, and hazardous waste lamps are already included on the federal list of universal wastes. The universal waste regulations in 40 CFR part 273 are a set of alternative hazardous waste management standards that operate in lieu of regulation under 40 CFR parts 260 through 272 for specified hazardous wastes.
Notably, four states, California, Colorado, Utah and New Mexico, already have universal waste aerosol can programs in place; and two more states, Ohio and Minnesota, have proposed to add aerosol cans to their universal waste regulations. The universal waste programs in all these states include streamlined management standards like 40 CFR part 273 for small and large quantity handlers of universal waste, and a one-year accumulation time limit for the aerosol cans. In addition, the four state universal waste programs, as well as Ohio's proposed regulations, set standards for puncturing and draining of aerosol cans by universal waste handlers.
More information on EPA's Universal Waste Program may be found here.
Contact ACA's Xavier Ferrier or Rhett Cash for more information.
Mar 13, 2018
Milwaukee HazWoper Refresher Seminar March 21, 2018
- Mandatory clean-up operations required by the government involving hazardous substances at uncontrolled hazardous waste sites.
- Corrective actions involving clean-up operations at RCRA sites
- Voluntary clean-up operations at RCRA sites
- Operations involving hazardous wastes that are conducted at treatment, storage, and disposal (TSDF) facilities
Mar 12, 2018
NEEDED: EHS Regulatory Content Project Manager $1000 finder fee!
Come work with an international team of experts building the world's largest set of regulatory data to keep the world safe and green. Nimonik is growing and needs an EHS Regulatory Content Project Manager who loves technology and data management!
Do you know the perfect candidate?
Receive $1000 if we hire someone you recommend.
Position: EHS Regulatory Content Project Manager
Salary: 30-70k CAD depending on location and experience
Job Description Summary
Create custom legal registers for Nimonik's customers by analyzing legislation to identify requirements that are applicable to their operations.
The job demands careful analysis of applicability and requirements of legislation to determine relevance. Nimonik customers you will work with will be in the US, Canada, Europe and Australia and will be certified ISO 14001, 50001 or 450001.
Larger projects will require you to train and manage junior regulatory analysts.
Read more and Apply now: https://nimonik.com/job/ehs-regulatory-content-project-manager/
Contact: Jonathan Brun
ca.linkedin.com/in/jonathanbrun
+1-514-712-0637
Seven years after Fukushima
Nuclear disaster aftermath affects environment and energy policies today
The Varsity: March 11, 2018 marks the seventh anniversary of the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster, the most significant nuclear incident since the 1986 Chernobyl explosion in Ukraine. The disaster has led to extensive scientific research in the affected areas in an effort to learn about its effects.
Triggered by a 9.0 magnitude earthquake, a massive tsunami off the coast of Japan destroyed the power and cooling systems of three nuclear reactors at the Fukushima Daiichi power plant. With the reactors melting down over the course of a few hours, the disaster caused significant environmental, economic, and psychological damage to the area and its residents.
Environmental research has examined the impact of the release of radioisotopes from the meltdown on terrestrial and marine wildlife. A review from 2015 observed declines in bird, butterfly, and cicada populations in Fukushima forests as well as abnormal morphological growth in aphids and trees.
In addition to environmental harm, researchers estimate that the total human mortality from the event will be around 10,000 with an additional lifetime cancer mortality of 1,500.

The remains of a house in Iwaki, Fukushima. ANDY TAKAGI/THE VARSITY
At the time of the event, over 150,000 people in the area were evacuated en masse, with many ending up in temporary housing. While Japanese authorities claim that the area is safe and are proceeding to move residents back to the area, people remain hesitant.
Skepticism about safety stems from recent reports of robots being destroyed within hours of being sent into the reactor buildings. Likewise, a recent Greenpeace Japan report claims that current radiation levels remain three times higher than government targets despite cleanup work in the area. This suggests that the area may not be habitable just yet.
Globally, there has been growing skepticism toward nuclear energy. While nuclear generation provides cheap electricity and does not emit greenhouse gases, a 2013 study examining 42 countries found that the Fukushima event has shifted views on nuclear energy toward the negative.
Japan shut down its nuclear power enterprise in the wake of the event and currently provides monthly updates to the International Atomic Energy Agency on the status of the Fukushima Daiichi. Germany has shut down several of its reactors and recently reaffirmed its commitment to phase out nuclear power by 2022.

Collected trash and radioactive dirt from government clean-up effort.
ANDY TAKAGI/THE VARSITY
Other countries appear open to the idea as well. South Korean President Moon Jae-in promised to eliminate both coal and nuclear power, though there are clear challenges to keeping this promise: nine reactors have opened in South Korea since 2000, and five are currently under construction. Japan has brought five reactors online as of September 2017, with more to come in the future.
Despite changing attitudes, not a lot has changed in relation to the production and generation of nuclear energy since the event, according to Steve Hoffman, an Assistant Professor in the Department of Sociology.
"Among the large nuclear producers, only two nations shifted their nuclear energy policies in a significant way in the wake of the Fukushima disaster – Japan and Germany… [However], the reductions of major producers like Japan and Germany has been offset by the increased production in China, which has been growing their nuclear fleet at an extremely rapid rate," wrote Hoffman.
Read on at: https://thevarsity.ca/2018/03/11/seven-years-after-fukushima/
Nonfatal Injuries among Law Enforcement Officers
Study provides estimates and trends of emergency department visits for both intentional and unintentional on-duty injuries
An estimated 669,100 law enforcement officers were treated in emergency departments across the nation for nonfatal injuries between 2003 and 2014, according to a study by researchers at the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH). The study, which is the first to examine nonfatal injuries among officers on a national scale, was published online this month in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine.
Law enforcement officers (LEOs) have historically high rates of fatal and nonfatal injuries. The new research shows that officers are three times more likely to sustain a nonfatal injury than all other U.S. workers, and is the first to capture nonfatal injuries sustained from assaults and unintentional injuries such as accidental falls or motor vehicle crashes.
"Studies based on evidence are an important feature of public health and this principle extends to studying the law enforcement community and their work," said NIOSH Director John Howard, M.D. "The safety and health of both police and citizens depend on understanding how policing tactics impact officer and citizen injuries."
The study researchers, whose aim was to provide national estimates and trends of nonfatal injuries to law enforcement officers from 2003 – 2014, found the following:
- The LEO nonfatal injury trend increased across the 12-year period studied; this is in contrast with the trend for all other U.S. workers which significantly decreased.
- Assault-related injury rates significantly increased almost 10% annually from 2003 to 2011.
- The three leading reasons for on-duty injuries were assaults & violent acts (36%), bodily reactions & exertion from running or other repetitive motions (15%), and transportation incidents (14%).
The study used nonfatal injury data from the National Electronic Injury Surveillance System – Occupational Supplement (NEISS-Work). Data were obtained for injuries treated in U.S. emergency departments from 2003-2014.
To access the paper, please visit Nonfatal injuries to law enforcement officers treated in U.S. emergency departments: A rise in assaults
NIOSH Releases Updated Strategic Plan
In February, NIOSH released its updated Strategic Plan for fiscal years 2019–2023. This new plan covers the breadth of the research and service work at NIOSH and is organized into the following seven strategic goals, representing the health and safety issues facing the U.S. workforce:
- Reduce occupational cancer, cardiovascular disease, adverse reproductive outcomes, and other chronic diseases.
- Reduce occupational hearing loss.
- Reduce occupational immune, infectious, and dermal disease.
- Reduce occupational musculoskeletal disorders.
- Reduce occupational respiratory disease.
- Improve workplace safety to reduce traumatic injuries.
- Promote safe and healthy work design and well-being.
To support the seven strategic goals, NIOSH created two sets of intermediate and activity goals. The first set is comprised of research goals that are shared by multiple NIOSH programs, fostering collaboration across the Institute. Sector, cross-sector, and core and specialty programs first reviewed the draft National Occupational Research Agendas (NORA) for the third decade of NORA written by NORA councils, thinking about which objectives or parts of objectives NIOSH is well suited to undertake. NIOSH programs also weighed additional factors, such as mandates from Congress and the Executive Branch, stakeholder input, innovative ideas, and emerging issues. The programs developed research priorities from these inputs using the Burden, Need, and Impact Method (BNI Method). This method helps NIOSH to decide how to allocate its research dollars since NIOSH is always faced with more research needs than we have resources to address. While the BNI method has been used at the individual project level for the past several years, this is the first time it has been used on a broader programmatic level.
Read on:
New NIOSH Studies Examine Hearing Loss Prevalence in Workers
This study found that the prevalence of hearing loss among noise-exposed workers in the Agriculture, Forestry, Fishing and Hunting (AFFH) sector is 15%. However, when researchers examined industries within the sector, they found as many as 36%—or 1 in 3 noise-exposed workers—have hearing loss. This is the first study to estimate prevalence and risk for hearing loss for subsectors within the Agriculture, Forestry, Fishing and Hunting industry sector. The study was published in the American Journal of Industrial Medicine. Learn more.- This study breaks down the prevalence of hearing loss experienced by workers in the Health Care and Social Assistance (HSA) sector. The overall prevalence of hearing loss among noise-exposed workers was found to be 19%, while some subsectors within the HSA had up to 31% prevalence of hearing loss. The study was published recently in the Journal of Occupational and Environmental Medicine. Learn more.
SBA Office of Advocacy - Regional Regulatory Roundtable - Milwaukee, WI
Mar 7, 2018
Final Rule: Definition of “Waters of the United States” Addition of Applicability Date to 2015 Clean Water Rule
Wisconsin Company Achieves Injury-Free Workplace with Help From On-Site Consultation Program
OSHA Announces Agency Goal to Reduce Trenching and Excavation Hazards
OSHA's Agency Priority Goal for 2018 aims to reduce trenching and excavation hazards. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, excavation and trench-related fatalities in 2016 were nearly double the average of the previous five years. OSHA's goal is to increase awareness of trenching hazards in construction, educate employers and workers on safe cave-in prevention solutions, and decrease the number of trench collapses.
OSHA plans to issue public service announcements, support the National Utility Contractors Association's 2018 Trench Safety Stand Down, update online resources on trench safety, and work with other industry associations and public utility companies to create an effective public-private effort to save lives. OSHA's trenching and excavation national emphasis program is also currently under revision. For more information on trench safety, visit OSHA's safety and health topics page.
Secretary of Labor Discusses Efforts to Protect Children from Lead Exposure
On Feb. 15, Secretary of Labor Alexander Acosta joined Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) Administrator Scott Pruitt and fellow Cabinet members to outline a federal strategy to reduce childhood lead exposure and associated health risks.
"Far too many Americans are exposed to lead in their workplace," said Labor Secretary Alexander Acosta. "Finding solutions to better protect these workers and minimize the amount of lead that is taken home, and potentially exposed to their children, is a priority."
OSHA's resource, If You Work Around Lead, Don't Take It Home!, highlights the dangers to children of lead being transported home from work, and offers precautions that can be taken.
For more information, read the EPA news release.